by Danish Ali Detho | O365 & Power Platform Solution Architect
MS Teams has become one of the most widely used tools for team collaboration and communication in organizations using Microsoft echo-system for their digital workspace. But when you need a quick and easy way to store and track some data, you probably turn to SharePoint Lists or Excel for the data storage. Although they are both tightly integrated with MS Teams but wouldn’t it be great if the solution completely lives within MS Teams. That’s where MS Dataverse for Teams comes in which is a cut-down and most importantly free version of Microsoft Dataverse that provides a low-code development environment for building Apps, Chatbots, and Flows all within Microsoft Teams.
It allows users to easily create data tables with an Excel-like experience, but with the benefit of a relational database that can handle much bigger datasets and manage relationships. In this blog, we will take a deep dive into MS Dataverse for Teams and how is it different from Dataverse, what are the main features and how to set up within your Teams environment.
What is MS Dataverse for Teams?
MS Dataverse for Teams provides citizen developers/business users a built-in, low-code data platform for Microsoft Teams where they can build applications that are accessed directly from Teams. It provides a subset of the functionality of Microsoft Dataverse (formerly known as CDS) for Teams users and the best part is that it comes free (with capacity limits) and doesn’t require any additional license. Each team has its own Dataverse and as soon as you create an application in Teams, a Dataverse will be built for that team for their applications which starts out as empty and you then build your own custom tables for your business objects and teams.
How is it different from MS Dataverse?
Microsoft Dataverse for Teams is a lite version of Dataverse (formerly known as the Common Data Service), which is the enterprise-grade data platform underneath Dynamics 365 and the full Power Platform. It provides some great features for building applications in MS Teams platform however it does lack some features which are available in the Dataverse which are covered below.
| Feature |
Dataverse for Teams |
MS Dataverse |
| Data types |
Supports Basic datatypes |
Supports Basic & Advanced data types (Customer, Accounts) |
| Relational storage |
Provides Relational storage (Tables) |
Provides Relational storage and Non-relational storage (Logs) |
| Common Data Model |
User table only |
Full support |
| Capacity |
Up to 1 million rows and
2000 API calls per day per user |
No specified limit on rows.
No specified limit of files or images.
2,000 API requests per day with the option of capacity add-ons. |
| Security |
Owner, Member, Guest roles
Share app with Azure AD group |
Extensive security options based on roles, business units & teams. |
| Clients |
Teams |
Teams, Power Apps, Power Apps portals, Dynamics 365, custom code |
| Custom development capability |
Not supported |
REST API, Software Development Kit (SDK), Plug-in Support |
| Solution for deployment |
Single unmanaged solution per environment |
Unlimited |
| Add-on capabilities |
Not available |
Workflows, Business rules, Calculations and rollup |
Main Benefits and Limitations of Microsoft Dataverse for Teams
Benefits
- Support to build low-code and no-code apps flows, and chatbots for and within Teams.
- No additional licensing is required to use.
- Guest users can run Apps and have access to the data they created.
- Core data capabilities from the same Dataverse platform.
- A new visual editor that makes it even easier to define and populate table data.
- Support for 5 teams plus 1 additional team for every 20 licensed users.
- Upgradability to MS Dataverse.
Limitations
- The maximum data size is 10GB + 2GB per Dataverse environment (max of 1TB total capacity per tenant).
- Apps are only accessible via the Teams App or mobile App.
- There is no API access to Dataverse for Teams data.
- Apps are only accessible via the Teams App or mobile App.
Setting up Dataverse for MS Teams
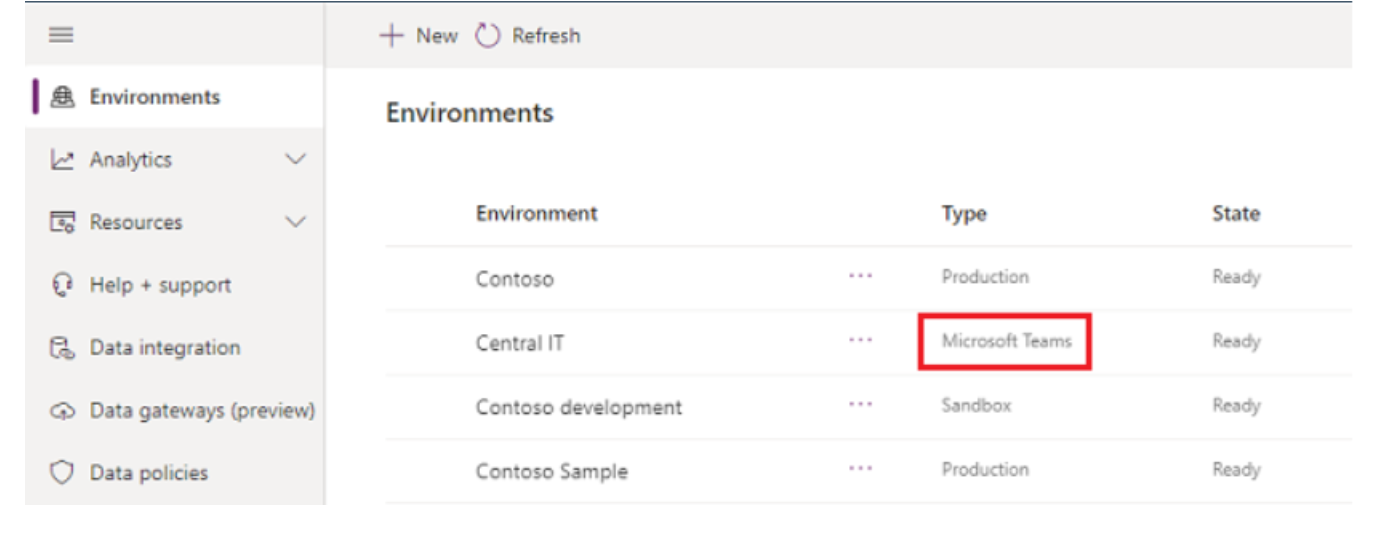
This part is super easy and the Dataverse for Teams environment is automatically created when you create the first App in Microsoft Teams or install a Power Apps app from the app catalogue for the first time. Each team can have one environment, and all data, apps, and flows created inside a team are available within the MS Team’s Dataverse. Power platform Admins can see all the MS Teams Dataverse instances created by going to Power platform admin -> Environments.
Conclusion
Microsoft Dataverse for Teams provides a super easy and convenient way to create Apps that completely lives within MS Teams platform which also supports relational data storage, rich data types, enterprise-grade governance, and one-click solution deployment. It does lack some important features which are available in MS Dataverse like core tables representing common business objects but they are on the roadmap for Dataverse for Teams and will be available soon. If you are looking to build an app and keep your data stored in one place where you are already working every day i.e. MS Teams along with associated collaboration and documents then MS Dataverse for Teams is the way to go.